This article is adapted from a panel discussion organized by PALO IT.
- Moderator: Jeremy Chu, Head of Data and AI, PALO IT
- Panelists: Dr Martin Saerbeck, CTO and Co-Founder of AIQURIS, a TÜV SÜD Venture & David Wilkins, Founder at Bamboo Code Technology & Partner
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the business landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency. However, successful AI integration requires careful consideration of mindset, trust, and governance. This post explores key aspects of AI adoption, drawing insights from recent discussions on the topic.
Given the increasing importance of AI, regulations and legislation in Singapore are also rapidly catching up. Recent initiatives demonstrate Singapore's commitment to AI safety and responsible development, not just for its citizens but on a global scale. These include the Global AI Assurance Pilot for GenAI application testing, a Joint Testing Report with Japan focusing on multilingual model safety, and the Singapore AI Safety Red Teaming Challenge Evaluation Report, which addresses cultural biases in LLMs within the Asia Pacific region. These efforts, announced at the AI Action Summit in Paris, underscore Singapore's proactive role in shaping international AI governance and fostering a trusted AI ecosystem, balancing innovation with crucial safeguards.
With this evolving landscape in mind, let's delve deeper into the key aspects of AI adoption within organizations.
 Embracing the Right Mindset
Embracing the Right Mindset
One of the foundational elements for successful AI implementation is cultivating the right organizational mindset. There are two common mindsets that organizations can embody when considering AI adoption: a skeptical/hesitant mindset and a growth-oriented/embracing mindset. Cultural acceptance is crucial. As one expert noted in a recent panel discussion:
"If you don't have the mindset of wanting to embrace AI, it doesn't really matter what you do - it's never really going to take off."
Digging Deeper:
- Skeptical Mindset: This mindset is often characterized by fear of job displacement, concerns about data security, and a general distrust of new technologies. Overcoming this requires education, transparency, and demonstrating the value of AI through pilot projects and clear use cases.
- Growth-Oriented Mindset: This mindset views AI as an opportunity to enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and drive innovation. Fostering this requires strong leadership support, investment in training, and creating a culture of experimentation and learning.
- Cultural Acceptance: Creating a culture that's receptive to AI involves addressing employee concerns, providing opportunities for upskilling, and celebrating early successes. It's about making AI a part of the organizational DNA.
AI as a Tool, Not a Replacement
It's essential to understand AI's role within the organization. AI should be viewed as a tool to augment human capabilities, not as a complete replacement for human decision-making. Strategic decisions should remain the purview of executive management, with AI supporting tasks such as market research and analysis.
"Human decision-making is not going to go away, but AI is a tool that can do some of the grunt work, do some of the background market research... it's here to help us, let's see how we're going to use it."
Elaborating on AI's Role:
- Focus on Augmentation: Identify tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, or data-intensive and explore how AI can automate or streamline them. Examples include data analysis, report generation, customer service inquiries, and fraud detection.
- Strategic Decision Support: Use AI to provide insights and recommendations to support strategic decision-making. AI can analyze market trends, identify competitive threats, and assess potential risks.
- Skill Development: Invest in training programs to equip employees with the skills needed to work effectively with AI systems. This includes data literacy, critical thinking, and AI ethics.
- Chopsticks Analogy: Emphasizing that AI is a tool, one of the panel experts analogized it to chopsticks - while they can enhance one's ability to eat, they are useless if one doesn't know how to use them. Organizations must consider what skills their employees need to effectively use AI.
Building Trust in AI Systems
Trust is paramount when integrating AI into critical business processes. Several factors contribute to building trust in AI systems.

Building trust in AI systems hinges on several key factors. First, consistency is paramount; AI systems must demonstrate reliable outputs. Second, alignment with expectations is crucial, ensuring that the AI's output aligns with professional expertise. Third, clear accountability frameworks are necessary to address errors and promote responsible usage. Fourth, while the inner workings of AI models may be complex, transparency in processes and decision-making builds confidence. Finally, robust governance structures are essential for managing AI risks and ensuring compliance.
Addressing AI Limitations
It's important to acknowledge the limitations of AI, including the potential for "hallucinations" or errors. Critical thinking is essential when evaluating AI outputs, and human oversight remains necessary. A balance must be struck between innovation and reliability.
Focusing on Limitations:
- AI Hallucinations: Be aware that AI systems can sometimes generate inaccurate or nonsensical outputs. Implement checks and balances to detect and correct these errors.
- Critical Thinking: Train employees to critically evaluate AI outputs and not blindly accept them as truth. Encourage them to question assumptions and challenge findings.
- Human Oversight: Maintain human oversight of AI systems, particularly in critical decision-making processes. Ensure that humans have the final say and can override AI recommendations.
- Grains of Sand Analogy: One expert analogized that AI systems are like billions of grains of sand - each grain is essential, but if something goes wrong, it is very difficult to determine the issue and fix it.
Navigating Regulatory and Governance Considerations
Regulatory compliance is a significant consideration, particularly for financial institutions and other heavily regulated industries. How does that look like?
- Outcome-Based Regulation:Focus on the desired outcomes of AI systems rather than prescribing specific technologies or approaches.
- Risk-Based Frameworks:Identify and assess the potential risks associated with AI systems and implement appropriate mitigation measures.
- Clear Documentation:Maintain detailed documentation of AI system design, development, and deployment processes.
- Accountability Structures:Establish clear lines of accountability for AI system performance and compliance.
- Human-in-the-Loop Processes:Incorporate human review and oversight into AI decision-making processes, particularly in high-stakes situations.
The Rise of AI Agents
AI agents represent a significant evolution in AI capabilities. Unlike traditional AI, which is task-specific, AI agents can handle multi-step processes without explicit instructions. However, this increased autonomy also presents challenges in terms of understanding and governing AI decision-making.
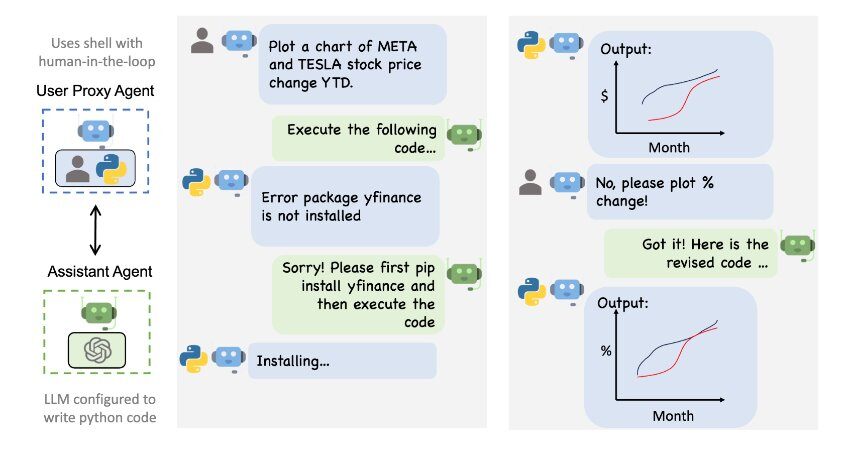
Understanding AI Agents:
- Autonomous Problem Solving: AI agents can analyze complex problems, develop solutions, and execute them without human intervention.
- Challenge of Explainability: The decision-making processes of AI agents can be difficult to understand, making it challenging to ensure accountability and transparency.
- Governance and Control: Establish robust governance frameworks to manage the risks associated with autonomous AI agents.
Conclusion
AI offers tremendous potential for driving innovation and improving efficiency. However, successful AI adoption requires a strategic approach that considers mindset, trust, governance, and human oversight. By embracing AI as a tool, fostering a culture of trust, and establishing clear guidelines, organizations can harness the power of AI while mitigating its risks. Accountability for decisions must remain with humans.
Want to learn how you can build better AI systems within your organization that effectively address these key considerations? Talk to us today to explore tailored strategies for AI implementation that maximize benefits while ensuring responsible and ethical use.

